New York City state income tax is one of the most critical financial obligations for residents and businesses in the city. Whether you're a new resident or a seasoned taxpayer, understanding how this tax works is essential for financial planning and compliance. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of NYC state income tax, ensuring you have all the information you need to manage your finances effectively.
Living in New York City comes with unique financial responsibilities. Among these is the requirement to pay state and local income taxes. These taxes contribute significantly to the city's infrastructure, public services, and overall quality of life. However, navigating the tax system can be complex, especially for those unfamiliar with the process.
Our goal is to simplify the complexities of NYC state income tax. This article will provide a detailed overview, including rates, filing requirements, deductions, and tips for minimizing your tax burden. By the end of this guide, you will have a clear understanding of your obligations and how to optimize your tax strategy.
Read also:Exploring The Life And Achievements Of Larry Finks Daughter
Table of Contents
- Introduction to NYC State Income Tax
- NYC State Income Tax Rates
- Who Needs to File NYC State Income Tax?
- Understanding Tax Deductions and Credits
- Filing Forms and Deadlines
- Penalties for Late Filing
- Residency Rules and Tax Implications
- Business Taxes in NYC
- Tips for Reducing Your Tax Liability
- Useful Resources for Taxpayers
Introduction to NYC State Income Tax
New York City state income tax is a combination of state and local taxes that residents must pay annually. Unlike other cities, NYC imposes an additional local income tax on top of the state tax. This dual tax structure means that residents face higher tax burdens compared to those in other states.
The tax rates vary depending on income levels, marital status, and residency status. Understanding these factors is crucial for accurate tax planning. Additionally, New York City offers several deductions and credits that can help reduce your tax liability, making it important to familiarize yourself with these options.
Why NYC State Income Tax Matters
Taxes collected from residents fund essential services such as public transportation, education, healthcare, and public safety. By paying your fair share, you contribute to the city's growth and development. However, it's equally important to ensure that you're not overpaying and are taking full advantage of available deductions and credits.
NYC State Income Tax Rates
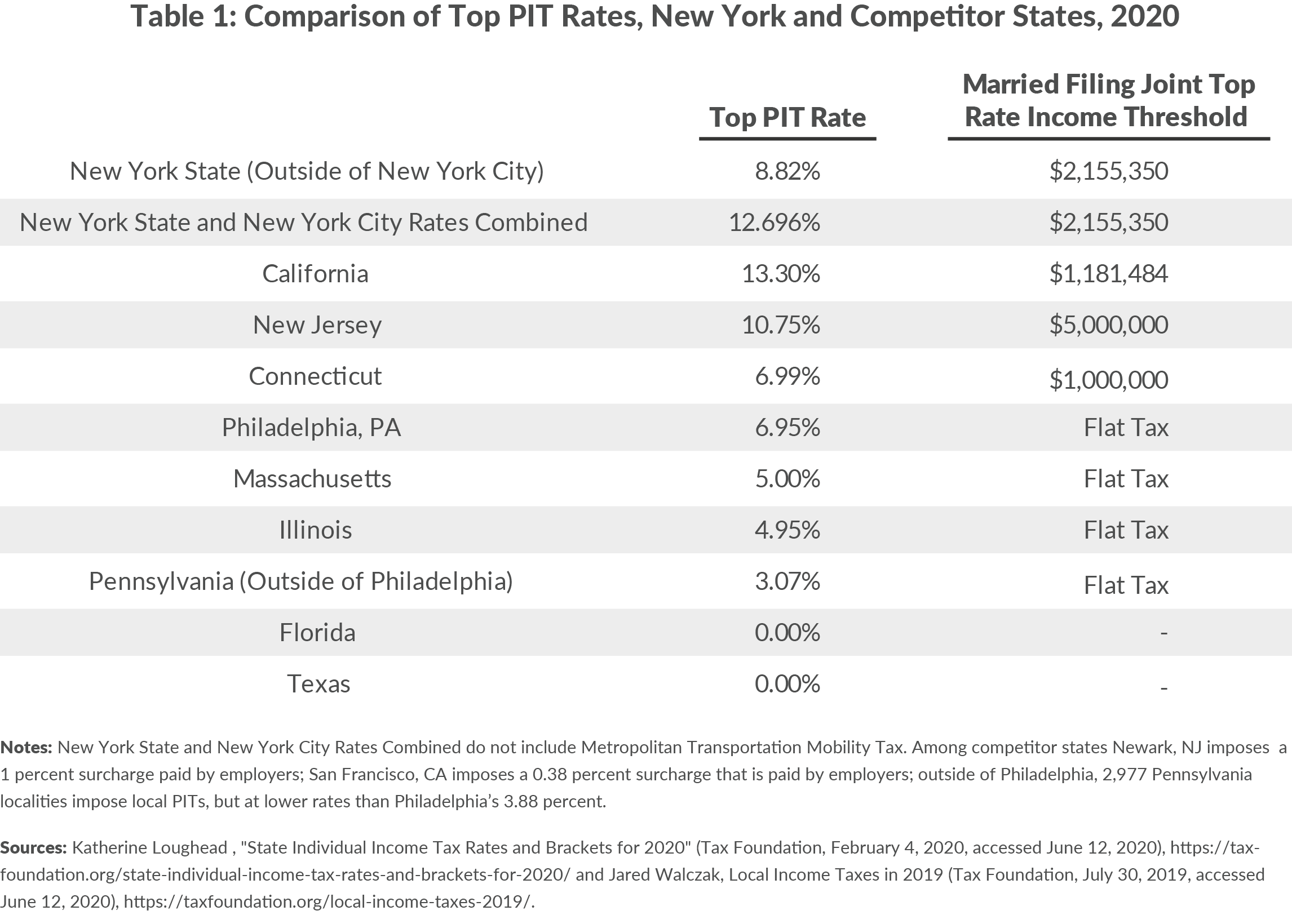
The tax rates for New York City residents are progressive, meaning they increase with income. As of 2023, the state income tax rates range from 4% to 8.82%, depending on your income bracket. Meanwhile, the NYC local income tax rates range from 2.907% to 3.876% for single filers and 3.059% to 4.355% for married filers.
Income Brackets and Rates
- State Tax Rate: 4% for incomes up to $8,500
- State Tax Rate: 4.5% for incomes between $8,501 and $11,700
- City Tax Rate: 2.907% for incomes up to $12,000
- City Tax Rate: 3.059% for incomes between $12,001 and $25,000
These rates highlight the importance of understanding your income bracket to estimate your tax liability accurately.
Who Needs to File NYC State Income Tax?
Not everyone living in New York City is required to file state income tax. Generally, individuals who earn more than the standard deduction must file a tax return. For example, single filers with an income exceeding $12,950 and married couples filing jointly with an income over $25,900 need to file.
Read also:Exploring The Early Life Of Michael Lavaughn Robinson
Residency Status and Filing Requirements
Your residency status determines whether you need to file as a resident, non-resident, or part-year resident. Full-time residents are subject to both state and local taxes, while non-residents only pay state taxes on income earned in New York.
Understanding Tax Deductions and Credits
New York City offers several deductions and credits to help taxpayers reduce their liability. Some of the most common deductions include the standard deduction, itemized deductions, and personal exemptions. Credits such as the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) and Child Tax Credit can also significantly lower your tax bill.
Key Deductions to Consider
- Standard Deduction: Available to all taxpayers who do not itemize
- Itemized Deductions: Includes mortgage interest, charitable contributions, and state taxes paid
- Personal Exemptions: Allows taxpayers to deduct a fixed amount for themselves and dependents
Filing Forms and Deadlines
Filing your NYC state income tax involves using specific forms provided by the New York State Department of Taxation and Finance. The most common forms include IT-201 for resident filers and IT-203 for non-resident filers. The deadline for filing is typically April 15th, although extensions can be requested.
Steps to File Your Taxes
- Gather all necessary documents, including W-2 forms and 1099s
- Choose the appropriate filing status
- Complete the required forms accurately
- Submit your return by the deadline
Penalties for Late Filing
Failing to file your NYC state income tax on time can result in significant penalties and interest charges. The late filing penalty is 5% of the unpaid tax for each month or part of a month the return is late, up to a maximum of 25%. Additionally, interest is charged on any unpaid tax at a rate determined by the state.
Avoiding Penalties
To avoid penalties, ensure you file your taxes on time or request an extension if necessary. If you owe taxes, pay them by the deadline to avoid interest charges. Keeping accurate records and consulting a tax professional can also help prevent mistakes that lead to penalties.
Residency Rules and Tax Implications
Your residency status plays a crucial role in determining your tax obligations. Full-time residents are subject to both state and local taxes, while part-year residents pay taxes based on the portion of the year they lived in New York City. Non-residents only pay state taxes on income earned within the city.
Determining Your Residency Status
To qualify as a resident, you must maintain a permanent place of abode in New York City and spend more than 183 days there during the tax year. If you split your time between multiple locations, it's essential to track your days in the city to determine your residency status accurately.
Business Taxes in NYC
Businesses operating in New York City are also subject to state and local taxes. These include corporate income tax, sales tax, and payroll taxes. The rates and requirements vary depending on the type of business and its structure.
Tax Obligations for Businesses
- Corporate Income Tax: Applied to profits earned by corporations
- Sales Tax: Charged on goods and services sold within the city
- Payroll Taxes: Includes unemployment insurance and workers' compensation
Tips for Reducing Your Tax Liability
While paying taxes is a legal obligation, there are strategies you can use to reduce your liability. These include maximizing deductions, claiming available credits, and planning your finances strategically.
Strategies for Tax Reduction
- Itemize deductions if they exceed the standard deduction
- Claim all eligible credits, such as the EITC
- Contribute to retirement accounts to lower taxable income
Useful Resources for Taxpayers
For additional information and guidance, consider utilizing resources provided by the New York State Department of Taxation and Finance and the Internal Revenue Service. These organizations offer detailed guides, calculators, and customer support to assist taxpayers with their filings.
Recommended Resources
- New York State Department of Taxation and Finance
- IRS Publication 515: Withholding of Tax on Nonresident Aliens and Foreign Entities
- Tax Preparation Software: TurboTax, H&R Block
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding NYC state income tax is essential for all residents and businesses in the city. By familiarizing yourself with the rates, filing requirements, and available deductions, you can ensure compliance while minimizing your tax burden. We encourage you to take action by reviewing your financial situation, consulting a tax professional if needed, and utilizing the resources provided in this guide.
Don't forget to share this article with friends and family who may benefit from the information. Additionally, feel free to leave a comment below if you have questions or need further clarification. Together, we can make tax season a little less stressful and more manageable.
![NYC & NYS Tax Calculator [Interactive] Hauseit](https://www.hauseit.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/NYC-Income-Tax-Calculator.jpg)